Apush period 7 leq prompts – Embark on an enlightening journey through APUSH Period 7 with our comprehensive LEQ prompts. Designed to stimulate critical thinking and historical analysis, these prompts will equip you with the tools to conquer the challenges of the Advanced Placement United States History exam.
Delve into the intricacies of American imperialism, Progressivism, World Wars I and II, the Roaring Twenties, the New Deal, and the Cold War. Our expert guidance will empower you to unravel the complexities of these pivotal eras and craft compelling essays that showcase your understanding of history.
American Imperialism: Apush Period 7 Leq Prompts
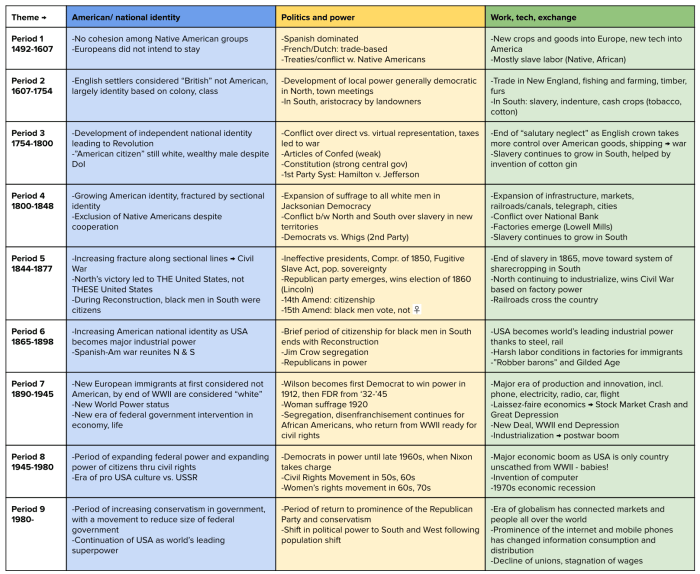
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the United States embarked on a period of rapid territorial expansion, acquiring vast overseas territories and establishing a global empire. This era of American imperialism was driven by a complex combination of factors, including economic, political, and cultural motivations.
Economic Factors
- Industrialization:The rapid industrialization of the United States created a surplus of goods that needed new markets. Imperialism provided access to new markets for American products and raw materials.
- Overseas Investment:American businesses sought to invest in overseas territories, particularly in Latin America and Asia, to exploit natural resources and labor.
Political Factors
- Manifest Destiny:The belief that the United States had a God-given right to expand its territory westward and across the oceans.
- National Prestige:Acquiring colonies was seen as a sign of national power and prestige, and it helped the United States to compete with other European powers.
- Geopolitical Concerns:The United States sought to control strategic territories, such as the Panama Canal, to protect its interests in the Western Hemisphere and beyond.
Cultural Factors, Apush period 7 leq prompts
- Social Darwinism:The belief that nations, like species, competed for survival, and that the United States was destined to dominate.
- Missionary Impulse:Many Americans believed that they had a moral obligation to spread Christianity and American values to the rest of the world.
Progressivism
The Progressive movement was a reform movement that emerged in the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Progressives sought to address the social and economic problems created by industrialization and urbanization, and to promote social justice and democracy.
Progressives believed that government should play an active role in regulating the economy and protecting the interests of the people. They supported a wide range of reforms, including antitrust laws, child labor laws, minimum wage laws, and women’s suffrage.
Key Ideas and Goals
The key ideas and goals of the Progressive movement included:
- Belief in the power of government to solve social and economic problems
- Support for social justice and democracy
- Promotion of economic regulation and consumer protection
- Advocacy for women’s suffrage and other reforms to improve the status of women
- Emphasis on education and public health
Methods of Reform
Progressives used a variety of methods to achieve their goals, including:
- Lobbying government officials
- Organizing boycotts and other forms of protest
- Running for political office
- Establishing settlement houses and other social welfare organizations
Successes and Limitations
The Progressive movement achieved a number of significant successes, including the passage of antitrust laws, child labor laws, minimum wage laws, and women’s suffrage. However, the movement also had some limitations.
One limitation was that Progressives were often unable to overcome the resistance of powerful business interests. Another limitation was that the movement was often divided by internal disagreements.
Despite these limitations, the Progressive movement had a lasting impact on American society. The reforms that Progressives achieved helped to improve the lives of millions of Americans and to lay the foundation for the modern welfare state.
World War I

World War I, a global conflict that engulfed Europe and beyond from 1914 to 1918, left an indelible mark on the course of human history. Its origins can be traced to a complex interplay of factors, including rising nationalism, imperialism, and a system of entangled alliances among European powers.
Causes and Outbreak
The seeds of World War I were sown in the decades leading up to the conflict. Rapid industrialization and economic growth fostered a sense of national pride and competition among European countries. Imperialism, the expansion of empires and the acquisition of colonies, further fueled tensions as nations sought to secure resources and establish spheres of influence.The
immediate catalyst for the war was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary by a Serbian nationalist in Sarajevo on June 28, 1914. Austria-Hungary, with the backing of Germany, issued an ultimatum to Serbia, which was supported by Russia.
The complex web of alliances drew the major European powers into the conflict, with Germany and Austria-Hungary on one side and Russia, France, and Great Britain on the other.
Major Events and Turning Points
The war began with a series of rapid German victories in the west, but the Allies managed to stabilize the front lines by the end of 1914. The conflict then settled into a bloody stalemate, characterized by trench warfare and high casualties.Key
turning points included the Battle of Verdun in 1916, one of the deadliest battles in history, and the entry of the United States into the war in 1917. The United States’ involvement brought fresh troops and supplies to the Allies, contributing to their eventual victory.
Impact on the United States and the World
World War I had a profound impact on the United States and the world. The war accelerated the country’s emergence as a global power and led to the creation of new international organizations, such as the League of Nations. However, it also resulted in significant loss of life and economic disruption, as well as the rise of totalitarian regimes in Europe.The
war left a lasting legacy of social and political upheaval, paving the way for the rise of fascism and communism and shaping the course of the 20th century.
The Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, a period of significant economic and social change in the United States, was characterized by rapid industrialization, technological advancements, and a cultural shift toward modernity.
Economic Changes
The decade witnessed a surge in economic growth driven by mass production, consumerism, and the rise of new industries such as automobiles and aviation. The stock market boomed, leading to widespread speculation and wealth accumulation.
Social Changes
The Roaring Twenties saw a transformation in social norms and values. Women gained greater independence and entered the workforce in increasing numbers. Urbanization accelerated, creating vibrant cities with diverse populations and entertainment options.
The Great Depression
The economic prosperity of the 1920s came to an abrupt end with the stock market crash of 1929, triggering the Great Depression. The crash led to a loss of confidence in the financial system, widespread unemployment, and a sharp decline in economic activity.
Cultural and Artistic Trends
The Roaring Twenties was a period of cultural and artistic experimentation. Jazz music became popular, and new literary styles such as the Lost Generation emerged. Art Deco architecture and design flourished, reflecting the optimism and modernity of the era.
The New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs and reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in response to the Great Depression. The New Deal aimed to provide relief to the unemployed, stimulate the economy, and reform the financial system.
Goals of the New Deal
- Provide relief to the unemployed and needy.
- Stimulate the economy and create jobs.
- Reform the financial system and prevent future economic crises.
Policies of the New Deal
The New Deal included a wide range of programs and reforms, including:
- The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), which provided jobs for young men in conservation projects.
- The Works Progress Administration (WPA), which provided jobs for unemployed workers on public works projects.
- The Social Security Act, which established a system of old-age insurance and unemployment benefits.
- The Glass-Steagall Act, which separated commercial and investment banking.
- The National Labor Relations Act, which protected the rights of workers to organize and bargain collectively.
Impact of the New Deal
The New Deal had a significant impact on the American economy and society. It provided relief to millions of unemployed workers and helped to stimulate the economy. It also led to important reforms in the financial system and labor relations.
Effectiveness of the New Deal
The New Deal is generally considered to have been effective in addressing the challenges of the Great Depression. It helped to reduce unemployment, stimulate the economy, and provide relief to the poor and needy. However, it did not completely end the Depression, and some of its programs were later found to be ineffective or unsustainable.
World War II
World War II, the most devastating conflict in human history, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The major participants were the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, and Japan) and the Allies (France, Great Britain, the Soviet Union, the United States, and China).
The war began with the German invasion of Poland in 1939 and ended with the surrender of Japan in 1945.The causes of World War II are complex and multifaceted. Some of the most important factors include the rise of fascism and militarism in Europe and Asia, the failure of the League of Nations to prevent aggression, and the economic depression of the 1930s.The
major events of World War II include the Battle of Britain, the invasion of the Soviet Union, the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Holocaust, and the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The war had a profound impact on the United States and the world, leading to the deaths of millions of people, the destruction of cities, and the redrawing of the political map of the world.
Causes of World War II
The rise of fascism and militarism in Europe and Asia was a major factor in the outbreak of World War II. In the 1920s and 1930s, fascist regimes came to power in Italy, Germany, and Japan. These regimes were characterized by their aggressive nationalism, their glorification of war, and their suppression of dissent.The
failure of the League of Nations to prevent aggression was another important factor in the outbreak of World War II. The League of Nations was an international organization that was created after World War I to prevent future wars. However, the League was unable to prevent the outbreak of World War II because it lacked the power to enforce its decisions.The
economic depression of the 1930s also contributed to the outbreak of World War II. The depression caused widespread unemployment and poverty, which led to social unrest and political instability. This instability made it easier for fascist regimes to come to power and to pursue aggressive policies.
Major Events of World War II
The Battle of Britain was a major turning point in World War II. In the summer of 1940, Germany launched a massive air campaign against Great Britain. The British Royal Air Force (RAF) successfully defended the country against the German Luftwaffe, and the battle was a major victory for the Allies.The
invasion of the Soviet Union by Germany in June 1941 was another major turning point in World War II. The German army was initially successful in its invasion, but the Soviet army was able to stop the German advance at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942-1943.
The Battle of Stalingrad was a major defeat for the Germans, and it marked the beginning of the end of the war.The attack on Pearl Harbor by Japan on December 7, 1941, brought the United States into World War II.
The attack was a surprise, and it resulted in the deaths of over 2,400 Americans. The United States quickly declared war on Japan, and the war in the Pacific began.The Holocaust was the systematic murder of millions of Jews by the Nazis during World War II.
For those tackling APUSH Period 7 LEQ prompts, understanding the historical context is crucial. One notable event is the USMC’s plans to field a new amphibious combat vehicle . This decision highlights the evolving nature of warfare and the USMC’s commitment to maintaining a strong amphibious capability.
By examining such developments, students can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of this historical period and its relevance to modern-day military operations.
The Holocaust was one of the most horrific crimes in human history, and it remains a reminder of the dangers of hatred and intolerance.The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by the United States in August 1945 ended World War II.
The bombings were devastating, and they resulted in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people. The bombings also led to the surrender of Japan and the end of the war.
Impact of World War II
World War II had a profound impact on the United States and the world. The war led to the deaths of millions of people, the destruction of cities, and the redrawing of the political map of the world.The United States emerged from World War II as a global superpower.
The war had boosted the American economy, and the United States had become the world’s leading economic and military power. The United States also played a major role in the creation of the United Nations, which was established to prevent future wars.The
war also had a profound impact on the world. The war led to the collapse of the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and the Netherlands. The war also led to the creation of new nations in Asia and Africa.
The war also led to the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as the two superpowers of the Cold War.
The Cold War
The Cold War was an era of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies. It began after the end of World War II in 1945 and continued until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. The conflict was never fought directly between the two superpowers, but instead took the form of political, economic, and propaganda warfare, as well as a series of proxy wars.
Causes and Origins
The Cold War emerged from a combination of factors, including:
- Ideological differences: The United States and the Soviet Union had fundamentally different political and economic systems. The United States promoted democracy and capitalism, while the Soviet Union advocated for communism and a centrally planned economy.
- Post-war tensions: The aftermath of World War II left Europe and Asia in ruins. The Soviet Union emerged as a major power in Eastern Europe, while the United States became the dominant force in Western Europe.
- Nuclear weapons: The development of nuclear weapons by both sides created a new level of fear and mistrust, as each superpower knew that it could destroy the other in a matter of minutes.
Essential Questionnaire
What are LEQ prompts?
LEQ (Long Essay Question) prompts are essay questions that require students to demonstrate their understanding of a specific historical topic by analyzing evidence and presenting a well-reasoned argument.
How can I prepare for APUSH Period 7 LEQ prompts?
Familiarize yourself with the content of Period 7, practice analyzing primary and secondary sources, and develop your writing skills by completing practice essays.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in APUSH Period 7 LEQ essays?
Avoid overgeneralizing, failing to provide specific evidence, or focusing solely on memorizing facts without demonstrating critical thinking.