Embarking on an exploration of active transport coloring answer key, we delve into the fascinating realm of cell transport, unraveling the intricate processes that govern the movement of molecules across cell membranes. This comprehensive guide illuminates the role of ATP in active transport, showcasing its significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating essential life functions.
Delving deeper into the intricacies of color theory, we uncover the fundamental principles that underpin the creation and perception of colors. The color wheel serves as a guiding tool, revealing the relationships between colors and their impact on visual perception.
Through practical examples, we demonstrate the power of color schemes and their ability to evoke emotions and convey messages.
Active Transport
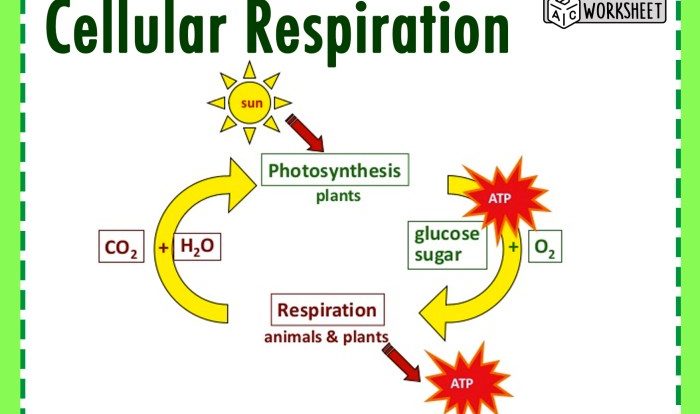
Active transport is a process by which cells move molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process requires energy, which is usually provided by ATP.
There are two main types of active transport: primary active transport and secondary active transport. Primary active transport uses ATP directly to power the movement of molecules across the membrane. Secondary active transport uses the energy stored in an electrochemical gradient to power the movement of molecules across the membrane.
Active transport is essential for a variety of cellular processes, including the uptake of nutrients, the removal of waste products, and the maintenance of cell volume.
Role of ATP in Active Transport, Active transport coloring answer key
ATP is the primary energy currency of cells. It is used to power a variety of cellular processes, including active transport. ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) to release energy. This energy is then used to power the movement of molecules across the membrane.
Examples of Active Transport in Living Organisms
Active transport is used in a variety of cellular processes, including:
- The uptake of nutrients into cells
- The removal of waste products from cells
- The maintenance of cell volume
- The transport of ions across membranes
FAQ Compilation: Active Transport Coloring Answer Key
What is the primary function of ATP in active transport?
ATP serves as the energy currency of cells, providing the necessary energy to drive the movement of molecules against their concentration gradients.
How does color theory influence the design of effective visual presentations?
Color theory provides a framework for understanding how colors interact and affect human perception. By utilizing color schemes and understanding the emotional impact of colors, designers can create visually appealing and impactful presentations.