Which of the atoms listed below has the smallest radius – Delving into the realm of atomic structures, we embark on an exploration to uncover which of the atoms listed below possesses the most diminutive radius. This fundamental property, known as atomic radius, plays a pivotal role in shaping the behavior and interactions of elements.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of atomic radius, we will unravel the factors that govern its variation across the periodic table. Through a comparative analysis, we will discern the periodic trends that dictate the radius of different elements, providing a comprehensive understanding of this crucial atomic characteristic.
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is a measure of the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom. It is typically measured in picometers (pm), where 1 pm is equal to 10^-12 meters. The atomic radius of an atom can vary depending on the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons in the atom.Atoms
with more electrons have a larger atomic radius than atoms with fewer electrons. This is because the electrons repel each other, causing the electron cloud to expand. Atoms with more protons have a smaller atomic radius than atoms with fewer protons.
This is because the protons attract the electrons, causing the electron cloud to contract. Atoms with more neutrons have a larger atomic radius than atoms with fewer neutrons. This is because the neutrons do not have a charge, so they do not affect the electron cloud.
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius
The atomic radius of an atom is affected by several factors, including:
- Number of electrons: Atoms with more electrons have a larger atomic radius than atoms with fewer electrons.
- Number of protons: Atoms with more protons have a smaller atomic radius than atoms with fewer protons.
- Number of neutrons: Atoms with more neutrons have a larger atomic radius than atoms with fewer neutrons.
- Effective nuclear charge: The effective nuclear charge is the net positive charge experienced by the electrons in an atom. The higher the effective nuclear charge, the smaller the atomic radius.
- Shielding effect: The shielding effect is the ability of inner electrons to shield outer electrons from the nucleus. The greater the shielding effect, the larger the atomic radius.
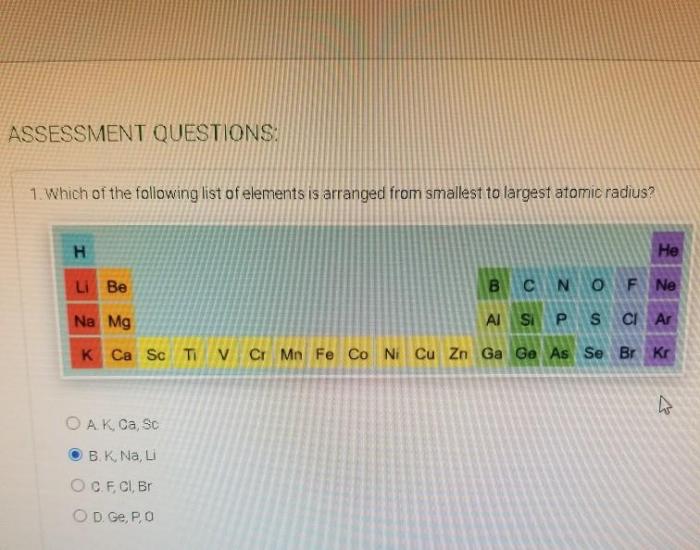
Periodic Trends in Atomic Radius
The atomic radius of an atom shows periodic trends across the periodic table. In general, the atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period and increases from top to bottom down a group.
- Across a period: The atomic radius decreases from left to right across a period because the number of protons increases while the number of electron shells remains the same. This causes the effective nuclear charge to increase, which attracts the electrons closer to the nucleus.
- Down a group: The atomic radius increases from top to bottom down a group because the number of electron shells increases while the number of protons remains the same. This causes the shielding effect to increase, which pushes the electrons further away from the nucleus.
Methods for Determining Atomic Radius
There are several methods for determining the atomic radius of an atom, including:
- X-ray crystallography: X-ray crystallography is a technique that uses X-rays to determine the structure of crystals. The atomic radius can be determined from the distance between the atoms in the crystal.
- Electron diffraction: Electron diffraction is a technique that uses electrons to determine the structure of atoms and molecules. The atomic radius can be determined from the diffraction pattern of the electrons.
- Neutron scattering: Neutron scattering is a technique that uses neutrons to determine the structure of atoms and molecules. The atomic radius can be determined from the scattering pattern of the neutrons.
Applications of Atomic Radius: Which Of The Atoms Listed Below Has The Smallest Radius

The atomic radius is a useful parameter in chemistry, materials science, and biology. It is used to:
- Predict the chemical reactivity of atoms: Atoms with a larger atomic radius are more reactive than atoms with a smaller atomic radius.
- Design new materials: The atomic radius can be used to design new materials with specific properties.
- Understand biological processes: The atomic radius can be used to understand biological processes, such as the folding of proteins.
Q&A
What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius refers to the distance from the nucleus of an atom to its outermost electron shell.
Which factors affect atomic radius?
Atomic radius is primarily influenced by the number of electron shells and the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electrons.
How does atomic radius vary across the periodic table?
Atomic radius generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.