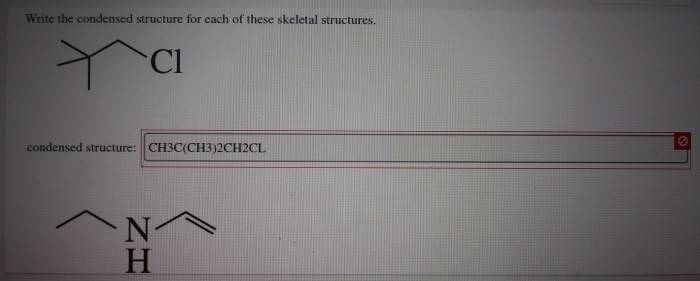
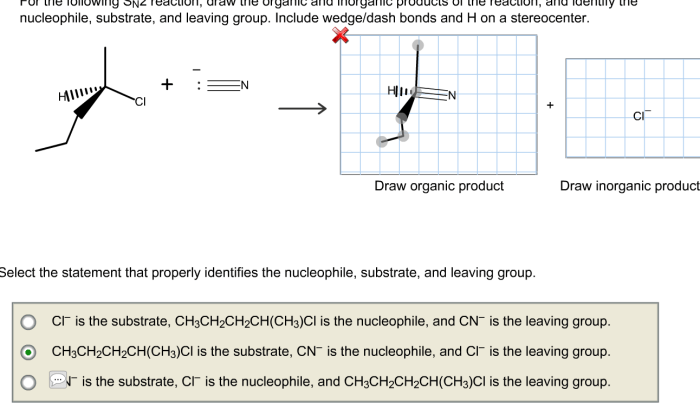
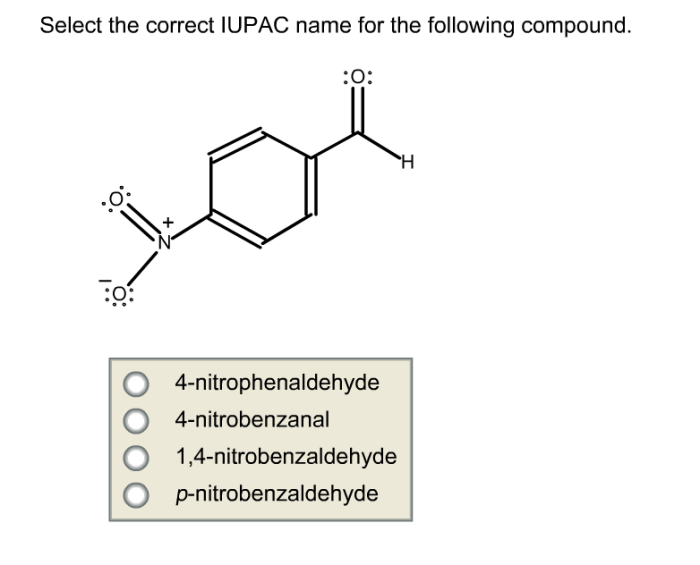
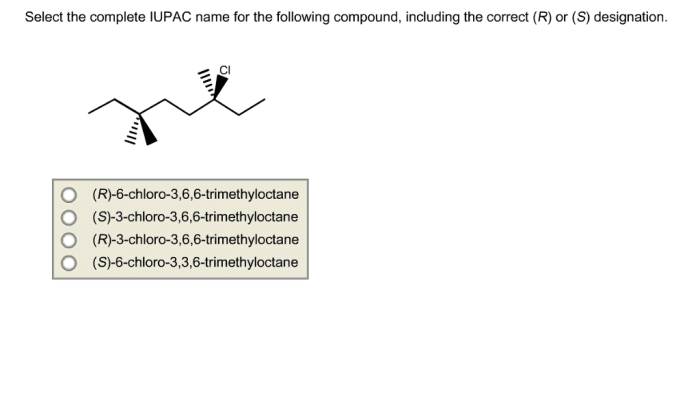
Select the correct iupac name for the following compound – Selecting the correct IUPAC name for an organic compound is crucial for precise communication and understanding in chemistry. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a systematic nomenclature system to assign unique and unambiguous names to organic compounds, ensuring consistency and clarity in scientific literature and research.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of IUPAC nomenclature, including the identification of functional groups, priority rules, and naming conventions. With a clear understanding of these principles, chemists can confidently assign IUPAC names to organic compounds, enabling effective communication and accurate documentation.
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) system provides a standardized set of rules for naming organic compounds. It assigns systematic, unambiguous names based on the structure and functional groups present in the molecule.
IUPAC names are constructed using the following principles:
- The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Functional groups are identified by their characteristic suffixes (-ane, -ene, -yne, -ol, -one, -al, -oic acid).
- Prefixes indicate the number and position of substituents on the parent chain.
- The name is assembled by combining the parent chain name, functional group suffix, and substituent prefixes.
Identifying Functional Groups: Select The Correct Iupac Name For The Following Compound
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within an organic compound that determine its chemical properties and reactivity. Common functional groups include:
- Alkanes: C-C single bonds (e.g., methane, ethane)
- Alkenes: C=C double bonds (e.g., ethene, propene)
- Alkynes: C≡C triple bonds (e.g., ethyne, propyne)
- Alcohols: -OH hydroxyl group (e.g., methanol, ethanol)
- Ketones: C=O carbonyl group (e.g., acetone, butanone)
- Aldehydes: -CHO carbonyl group (e.g., formaldehyde, acetaldehyde)
- Carboxylic acids: -COOH carboxyl group (e.g., formic acid, acetic acid)
Functional groups can be identified by their characteristic structural features, such as double bonds, triple bonds, hydroxyl groups, or carbonyl groups.
Priority Rules for IUPAC Nomenclature
When multiple functional groups are present in a molecule, priority rules are used to determine the principal functional group and the correct IUPAC name. The priority order is as follows:
- Carboxylic acids (-COOH)
- Esters (-COOR)
- Amides (-CONH2)
- Aldehydes (-CHO)
- Ketones (C=O)
- Alcohols (-OH)
- Ethers (-O-)
- Alkenes (C=C)
- Alkynes (C≡C)
- Alkanes (C-C)
The principal functional group determines the parent chain and the suffix of the IUPAC name. Substituents are then named and numbered according to their position on the parent chain.
IUPAC Naming Examples
| Structure | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|
| CH3CH2CH3 | Propane |
| CH3CH=CH2 | Propene |
| CH3CH2OH | Ethanol |
| CH3COCH3 | 2-Propanone |
| CH3CH2COOH | Butanoic acid |
| CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3 | 2-Butanol |
| CH3CH2CH=CH2 | 1-Butene |
| CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 | Pentane |
| CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH | Pentanoic acid |
Exceptions and Special Cases
There are some exceptions and special cases to the IUPAC naming rules, such as:
- Common names: Some compounds have well-established common names that are still used alongside their IUPAC names (e.g., methanol vs. methyl alcohol).
- Trivial names: Some compounds have trivial names that are not based on IUPAC rules (e.g., benzene, toluene).
- Branched alkyl groups: Branched alkyl groups are named as substituents using the prefix “iso-” or “neo-“.
- Multiple functional groups: When multiple functional groups are present, the IUPAC name is based on the highest priority functional group.
- Cyclic compounds: Cyclic compounds are named using the prefix “cyclo-” followed by the number of carbon atoms in the ring.
Expert Answers
What is the purpose of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature aims to provide a systematic and unambiguous naming system for organic compounds, ensuring clear and consistent communication among chemists.
How are functional groups identified in IUPAC nomenclature?
Functional groups are identified based on their characteristic structural features, such as the presence of specific atoms or bonds. Each functional group has a unique set of properties and reactivity patterns.
What are the priority rules used in IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature employs a set of priority rules to determine the principal functional group and the correct order of prefixes and suffixes in the name. These rules prioritize functional groups based on their seniority and the number of attached atoms.